Why the Mental Health of Liberal Girls Sank First and Fastest
Evidence for Lukianoff’s reverse CBT hypothesis
In May 2014, Greg Lukianoff invited me to lunch to talk about something he was seeing on college campuses that disturbed him. Greg is the president of FIRE (the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression), and he has worked tirelessly since 2001 to defend the free speech rights of college students. That almost always meant pushing back against administrators who didn’t want students to cause trouble, and who justified their suppression of speech with appeals to the emotional “safety” of students—appeals that the students themselves didn’t buy. But in late 2013, Greg began to encounter new cases in which students were pushing to ban speakers, punish people for ordinary speech, or implement policies that would chill free speech. These students arrived on campus in the fall of 2013 already accepting the idea that books, words, and ideas could hurt them. Why did so many students in 2013 believe this, when there was little sign of such beliefs in 2011?
Greg is prone to depression, and after hospitalization for a serious episode in 2007, Greg learned CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy). In CBT you learn to recognize when your ruminations and automatic thinking patterns exemplify one or more of about a dozen “cognitive distortions,” such as catastrophizing, black-and-white thinking, fortune telling, or emotional reasoning. Thinking in these ways causes depression, as well as being a symptom of depression. Breaking out of these painful distortions is a cure for depression.
What Greg saw in 2013 were students justifying the suppression of speech and the punishment of dissent using the exact distortions that Greg had learned to free himself from. Students were saying that an unorthodox speaker on campus would cause severe harm to vulnerable students (catastrophizing); they were using their emotions as proof that a text should be removed from a syllabus (emotional reasoning). Greg hypothesized that if colleges supported the use of these cognitive distortions, rather than teaching students skills of critical thinking (which is basically what CBT is), then this could cause students to become depressed. Greg feared that colleges were performing reverse CBT.
I thought the idea was brilliant because I had just begun to see these new ways of thinking among some students at NYU. I volunteered to help Greg write it up, and in August 2015 our essay appeared in The Atlantic with the title: The Coddling of the American Mind. Greg did not like that title; his original suggestion was “Arguing Towards Misery: How Campuses Teach Cognitive Distortions.” He wanted to put the reverse CBT hypothesis in the title.
After our essay came out, things on campus got much worse. The fall of 2015 marked the beginning of a period of protests and high-profile conflicts on campus that led many or most universities to implement policies that embedded this new way of thinking into campus culture with administrative expansions such as “bias response teams” to investigate reports of “microaggressions.” Surveys began to show that most students and professors felt that they had to self-censor. The phrase “walking on eggshells” became common. Trust in higher ed plummeted, along with the joy of intellectual discovery and sense of goodwill that had marked university life throughout my career.
Greg and I decided to expand our original essay into a book in which we delved into the many causes of the sudden change in campus culture. Our book focused on three “great untruths” that seemed to be widely believed by the students who were trying to shut down speech and prosecute dissent:
1. What doesn’t kill you makes you weaker
2. Always trust your feelings
3. Life is a battle between good people and evil people.
Each of these untruths was the exact opposite of a chapter in my first book, The Happiness Hypothesis, which explored ten Great Truths passed down to us from ancient societies east and west. We published our book in 2018 with the title, once again, of The Coddling of the American Mind. Once again, Greg did not like the title. He wanted the book to be called “Disempowered,” to capture the way that students who embrace the three great untruths lose their sense of agency. He wanted to capture reverse CBT.
The Discovery of the Gender-by-Politics Interaction
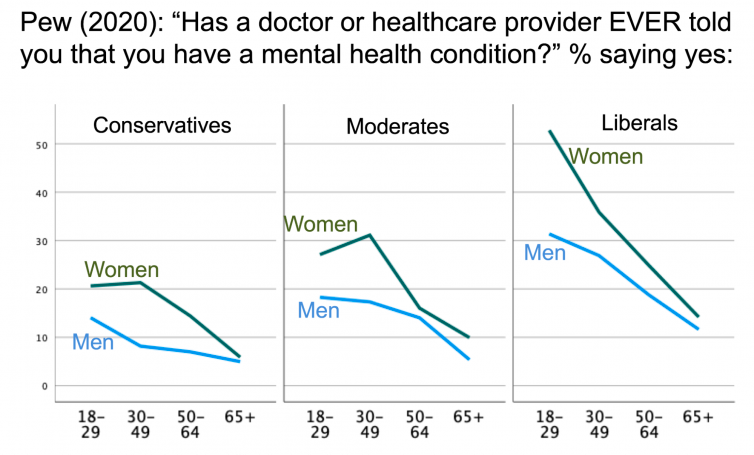
In September 2020, Zach Goldberg, who was then a graduate student at Georgia State University, discovered something interesting in a dataset made public by Pew Research. Pew surveyed about 12,000 people in March 2020, during the first month of the Covid shutdowns. The survey included this item: “Has a doctor or other healthcare provider EVER told you that you have a mental health condition?” Goldberg graphed the percentage of respondents who said “yes” to that item as a function of their self-placement on the liberal-conservative 5-point scale and found that white liberals were much more likely to say yes than white moderates and conservatives. (His analyses for non-white groups generally found small or inconsistent relationships with politics.)
I wrote to Goldberg and asked him to redo it for men and women separately, and for young vs. old separately. He did, and he found that the relationship to politics was much stronger for young (white) women. You can see Goldberg’s graph here, but I find it hard to interpret a three-way interaction using bar charts, so I downloaded the Pew dataset and created line graphs, which make it easier to interpret.
Here’s the same data, showing three main effects: gender (women higher), age (youngest groups higher), and politics (liberals higher). The graphs also show three two-way interactions (young women higher, liberal women higher, young liberals higher). And there’s an important three-way interaction: it is the young liberal women who are highest. They are so high that a majority of them said yes, they had been told that they have a mental health condition.
Figure 1. Data from Pew Research, American Trends Panel Wave 64. The survey was fielded March 19-24, 2020. Graphed by Jon Haidt.
In recent weeks—since the publication of the CDC’s report on the high and rising rates of depression and anxiety among teens—there has been a lot of attention to a different study that shows the gender-by-politics interaction: Gimbrone, Bates, Prins, & Keyes (2022), titled: “The politics of depression: Diverging trends in internalizing symptoms among US adolescents by political beliefs.” Gimbrone et al. examined trends in the Monitoring the Future dataset, which is the only major US survey of adolescents that asks high school students (seniors) to self-identify as liberal or conservative (using a 5-point scale). The survey asks four items about mood/depression.1 Gimbrone et al. found that prior to 2012 there were no sex differences and only a small difference between liberals and conservatives. But beginning in 2012, the liberal girls began to rise, and they rose the most. The other three groups followed suit, although none rose as much, in absolute terms, as did the liberal girls (who rose .73 points since 2010, on a 5-point scale where the standard deviation is .89).
Figure 2. Data from Monitoring the Future, graphed by Gimbrone et al. (2022). The scale runs from 1 (minimum) to 5 (maximum).
The authors of the study try to explain the fact that liberals rise first and most in terms of the terrible things that conservatives were doing during Obama’s second term, e.g.,
Liberal adolescents may have therefore experienced alienation within a growing conservative political climate such that their mental health suffered in comparison to that of their conservative peers whose hegemonic views were flourishing.
The progressive New York Times columnist Michelle Goldberg took up the question and wrote a superb essay making the argument that teen mental health is not and must not become a partisan issue. She dismissed Gimbrone et al.’s explanation as having a poor fit with their own data:
Barack Obama was re-elected in 2012. In 2013, the Supreme Court extended gay marriage rights. It was hard to draw a direct link between that period’s political events and teenage depression, which in 2012 started an increase that has continued, unabated, until today.
After examining the evidence, including the fact that the same trends happened at the same time in Britain, Canada, and Australia, Goldberg concluded that “Technology, not politics, was what changed in all these countries around 2012. That was the year that Facebook bought Instagram and the word “selfie” entered the popular lexicon.”
Journalist Matt Yglesias also took up the puzzle of why liberal girls became more depressed than others, and in a long and self-reflective Substack post, he described what he has learned about depression from his own struggles involving many kinds of treatment. Like Michelle Goldberg, he briefly considered the hypothesis that liberals are depressed because they’re the only ones who see that “we’re living in a late-stage capitalist hellscape during an ongoing deadly pandemic w record wealth inequality, 0 social safety net/job security, as climate change cooks the world,” to quote a tweet from the Washington Post tech columnist Taylor Lorenz. Yglesias agreed with Goldberg and other writers that the Lorenz explanation—reality makes Gen Z depressed—doesn’t fit the data, and, because of his knowledge of depression, he focused on the reverse path: depression makes reality look terrible. As he put it: “Mentally processing ambiguous events with a negative spin is just what depression is.”
Yglesias tells us what he has learned from years of therapy, which clearly involved CBT:
It’s important to reframe your emotional response as something that’s under your control:
Stop saying “so-and-so made me angry by doing X.”
Instead say “so-and-so did X, and I reacted by becoming angry.”
And the question you then ask yourself is whether becoming angry made things better? Did it solve the problem?
Yglesias wrote that “part of helping people get out of their trap is teaching them not to catastrophize.” He then described an essay by progressive journalist Jill Filipovic that argued, in Yglesias’s words, that “progressive institutional leaders have specifically taught young progressives that catastrophizing is a good way to get what they want.”
Yglesias quoted a passage from Filipovic that expressed exactly the concern that Greg had expressed to me back in 2014:
I am increasingly convinced that there are tremendously negative long-term consequences, especially to young people, coming from this reliance on the language of harm and accusations that things one finds offensive are “deeply problematic” or even violent. Just about everything researchers understand about resilience and mental well-being suggests that people who feel like they are the chief architects of their own life — to mix metaphors, that they captain their own ship, not that they are simply being tossed around by an uncontrollable ocean — are vastly better off than people whose default position is victimization, hurt, and a sense that life simply happens to them and they have no control over their response.
I have italicized Filipovic’s text about the benefits of feeling like you captain your own ship because it points to a psychological construct with a long history of research and measurement: Locus of control. As first laid out by Julian Rotter in the 1950s, this is a malleable personality trait referring to the fact that some people have an internal locus of control—they feel as if they have the power to choose a course of action and make it happen, while other people have an external locus of control—they have little sense of agency and they believe that strong forces or agents outside of themselves will determine what happens to them. Sixty years of research show that people with an internal locus of control are happier and achieve more. People with an external locus of control are more passive and more likely to become depressed.
How a Phone-Based Childhood Breeds Passivity
There are at least two ways to explain why liberal girls became depressed faster than other groups at the exact time (around 2012) when teens traded in their flip phones for smartphones and the girls joined Instagram en masse. The first and simplest explanation is that liberal girls simply used social media more than any other group. Jean Twenge’s forthcoming book, Generations, is full of amazing graphs and insightful explanations of generational differences. In her chapter on Gen Z, she shows that liberal teen girls are by far the most likely to report that they spend five or more hours a day on social media (31% in recent years, compared to 22% for conservative girls, 18% for liberal boys, and just 13% for conservative boys)2. Being an ultra-heavy user means that you have less time available for everything else, including time “in real life” with your friends. Twenge shows in another graph that from the 1970s through the early 2000s, liberal girls spent more time with friends than conservative girls.3 But after 2010 their time with friends drops so fast that by 2016 they are spending less time with friends than are conservative girls. So part of the story may be that social media took over the lives of liberal girls more than any other group, and it is now clear that heavy use of social media damages mental health, especially during early puberty.
But I think there’s more going on here than the quantity of time on social media. Like Filipovic, Yglesias, Goldberg, and Lukianoff, I think there’s something about the messages liberal girls consume that is more damaging to mental health than those consumed by other groups.
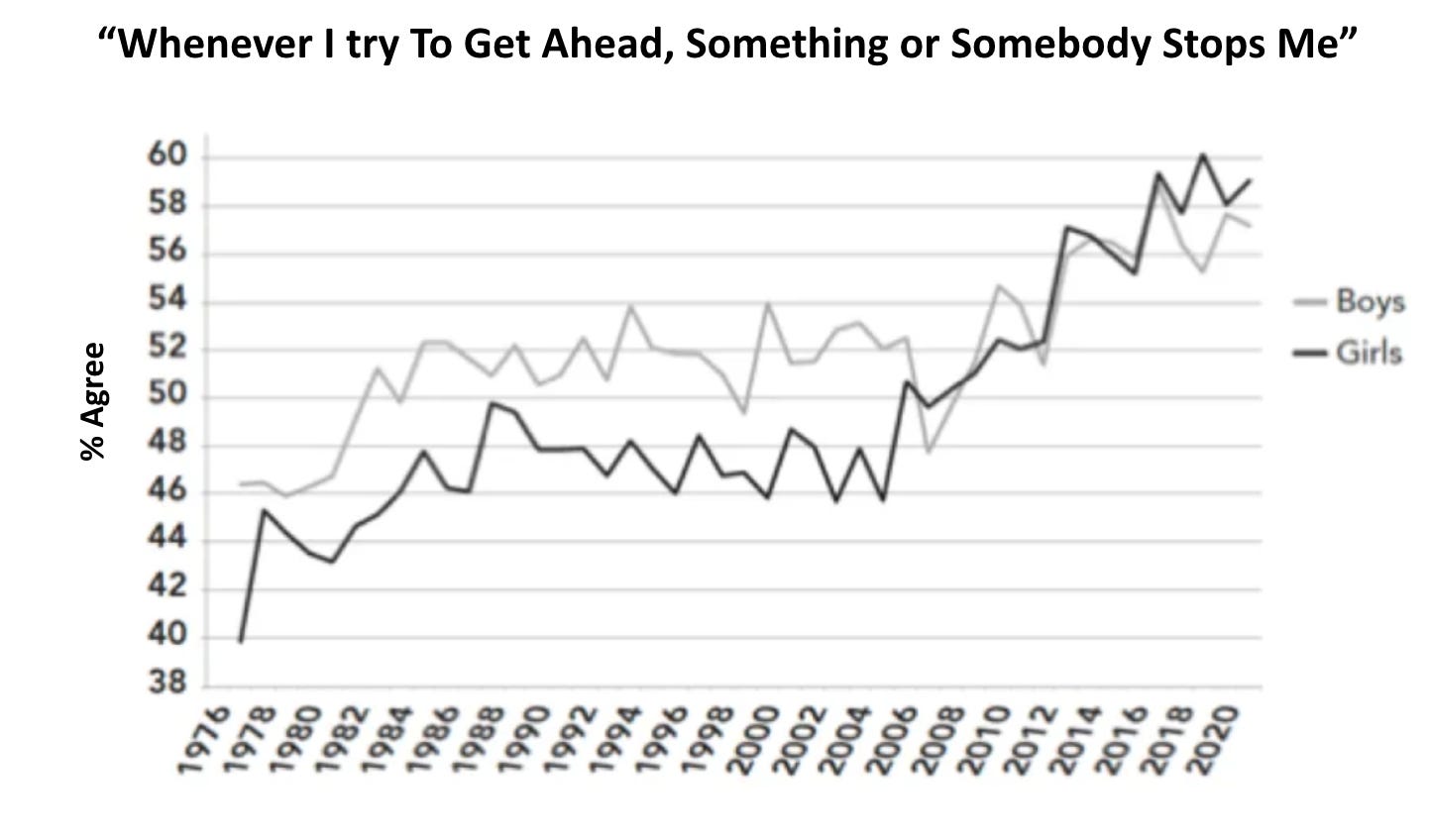
The Monitoring the Future dataset happens to have within it an 8-item Locus of Control scale. With Twenge’s permission, I reprint one such graph from Generations showing responses to one of the items: “Every time I try to get ahead, something or somebody stops me.” This item is a good proxy for Filipovic’s hypothesis about the disempowering effects of progressive institutions. If you agree with that item, you have a more external locus of control. As you can see in Figure 3, from the 1970s until the mid-2000s, boys were a bit more likely to agree with that item, but then girls rose to match boys, and then both sexes rose continuously throughout the 2010s—the era when teen social life became far more heavily phone-based.
Figure 3. Percentage of boys and girls (high school seniors) who agree with (or are neutral about) the statement “Every time I try to get ahead, something or somebody stops me.”4 From Monitoring the Future, graphed by Jean Twenge in her forthcoming book Generations.
When the discussion of the gender-by-politics interaction broke out a few weeks ago, I thought back to Twenge’s graph and wondered what would happen if we broke up the sexes by politics. Would it give us the pattern in the Gimbrone et al. graphs, where the liberal girls rise first and most? Twenge sent me her data file (it’s a tricky one to assemble, across the many years), and Zach Rausch and I started looking for the interaction. We found some exciting hints, and I began writing this post on the assumption that we had a major discovery. For example, Figure 4 shows the item that Twenge analyzed. We see something like the Gimbrone et al. pattern in which it’s the liberal girls who depart from everyone else, in the unhealthy (external) direction, starting in the early 2000s.
Figure 4. Percentage of liberal and conservative high school senior boys (left panel) and girls (right panel) who agree with the statement “Every time I try to get ahead, something or somebody stops me.” From Monitoring the Future, graphed by Zach Rausch.5
It sure looks like the liberal girls are getting more external while the conservative girls are, if anything, trending slightly more internal in the last decade, and the boys are just bouncing around randomly. But that was just for this one item. We also found a similar pattern for a second item, “People like me don’t have much of a chance at a successful life.” (You can see graphs of all 8 items here.)
We were excited to have found such clear evidence of the interaction, but when we plotted responses to the whole scale, we found only a hint of the predicted interaction, and only in the last few years, as you can see in Figure 5. After trying a few different graphing strategies, and after seeing if there was a good statistical justification for dropping any items, we reached the tentative conclusion that the big story about locus of control is not about liberal girls, it’s about Gen Z as a whole. Everyone—boys and girls, left and right—developed a more external locus of control gradually, beginning in the 1990s. I’ll come back to this finding in future posts as I explore the second strand of the After Babel Substack: the loss of “play-based childhood” which happened in the 1990s when American parents (and British, and Canadian) stopped letting their children out to play and explore, unsupervised. (See Frank Furedi’s important book Paranoid Parenting. I believe that the loss of free play and self-supervised risk-taking blocked the development of a healthy, normal, internal locus of control. That is the reason I teamed up with Lenore Skenazy, Peter Gray, and Daniel Shuchman to found LetGrow.org.)
Figure 5. Locus of Control has shifted slightly but steadily toward external since the 1990s. Scores are on a 5-point scale from 1 = most internal to 5 = most external.
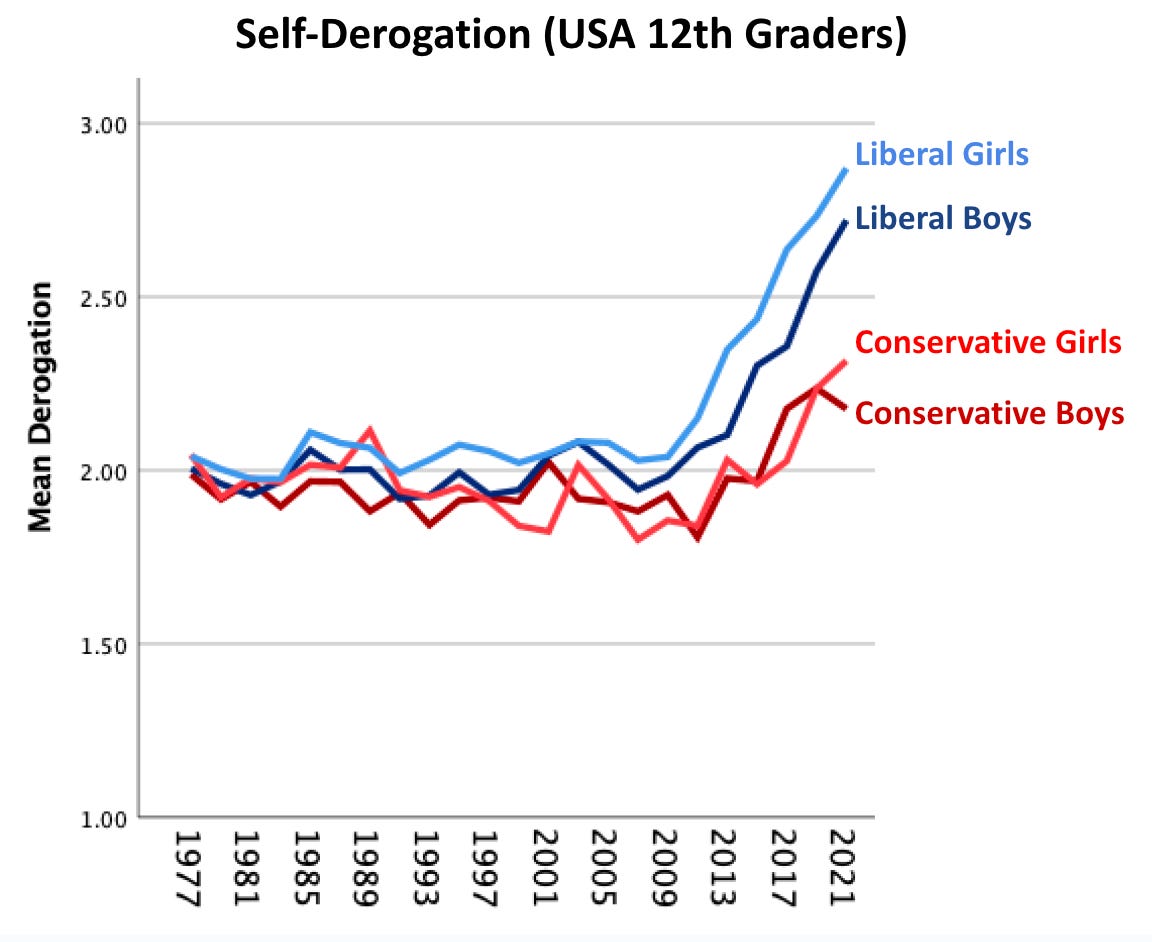
We kept looking in the Monitoring the Future dataset and the Gimbrone et al. paper for other items that would allow us to test Filipovic’s hypothesis. We found an ideal second set of variables: The Monitoring the Future dataset has a set of items on “self derogation” which is closely related to disempowerment, as you can see from the four statements that comprise the scale:6
I feel I do not have much to be proud of.
Sometimes I think I am no good at all.
I feel that I can't do anything right.
I feel that my life is not very useful.
Gimbrone et al. had graphed the self-derogation scale, as you can see in their appendix (Figure A.4). But Zach and I re-graphed the original data so that we could show a larger range of years, from 1977 through 2021. As you can see in Figure 6, we find the gender-by-politics interaction. Once again, and as with nearly all of the mental health indicators I examined in a previous post, there’s no sign of trouble before 2010. But right around 2012 the line for liberal girls starts to rise. It rises first, and it rises most, with liberal boys not far behind (as in Gimbrone et al.).
Figure 6. Self-derogation scale, averaging four items from the Monitoring the Future study. Graphed by Zach Rausch. The scale runs from 1 (strongly disagree with each statement) to 5 (strongly agree).
In other words, we have support for Filipovic’s “captain their own ship” concern, and for Lukianoff’s disempowerment concern: Gen Z has become more external in its locus of control, and Gen Z liberals (of both sexes) have become more self-derogating. They are more likely to agree that they “can’t do anything right.” Furthermore, most of the young people in the progressive institutions that Filipovic mentioned are women, and that has become even more true since 2014 when, according to Gallup data, young women began to move to the left while young men did not move either way. As Gen Z women became more progressive and more involved in political activism in the 2010s, it seems to have changed them psychologically. It wasn’t just that their locus of control shifted toward external—that happened to all subsets of Gen Z. Rather, young liberals (including young men) seem to have taken into themselves the specific depressive cognitions and distorted ways of thinking that CBT is designed to expunge.
But where did they learn to think this way? And why did it start so suddenly around 2012 or 2013, as Greg observed, and as Figures 2 and 6 confirm?
Tumblr Was the Petri Dish for Disempowering Beliefs
I recently listened to a brilliant podcast series, The Witch Trials of J. K. Rowling, hosted by Megan Phelps-Roper, created within Bari Weiss’s Free Press. Phelps-Roper interviews Rowling about her difficult years developing the Harry Potter stories in the early 1990s, before the internet; her rollout of the books in the late 90s and early 2000s, during the early years of the internet; and her observations about the Harry Potter superfan communities that the internet fostered. These groups had streaks of cruelty and exclusion in them from the beginning, along with a great deal of love, joy, and community. But in the stunning third episode, Phelps-Roper and Rowling take us through the dizzying events of the early 2010s as the social media site Tumblr exploded in popularity (reaching its peak in early 2014), and also in viciousness. Tumblr was different from Facebook and other sites because it was not based on anyone’s social network; it brought together people from anywhere in the world who shared an interest, and often an obsession.
Phelps-Roper interviewed several experts who all pointed to Tumblr as the main petri dish in which nascent ideas of identity, fragility, language, harm, and victimhood evolved and intermixed. Angela Nagle (author of Kill All Normies) described the culture that emerged among young activists on Tumblr, especially around gender identity, in this way:
There was a culture that was encouraged on Tumblr, which was to be able to describe your unique non-normative self… And that’s to some extent a feature of modern society anyway. But it was taken to such an extreme that people began to describe this as the snowflake [referring to the idea that each snowflake is unique], the person who constructs a totally kind of boutique identity for themselves, and then guards that identity in a very, very sensitive way and reacts in an enraged way when anyone does not respect the uniqueness of their identity.
Nagle described how on the other side of the political spectrum, there was “the most insensitive culture imaginable, which was the culture of 4chan.” The communities involved in gender activism on Tumblr were mostly young progressive women while 4Chan was mostly used by right-leaning young men, so there was an increasingly gendered nature to the online conflict. The two communities supercharged each other with their mutual hatred, as often happens in a culture war. The young identity activists on Tumblr embraced their new notions of identity, fragility, and trauma all the more tightly, increasingly saying that words are a form of violence, while the young men on 4chan moved in the opposite direction: they brandished a rough and rude masculinity in which status was gained by using words more insensitively than the next guy. It was out of this reciprocal dynamic, the experts on the podcast suggest, that today’s cancel culture was born in the early 2010s. Then, in 2013, it escaped from Tumblr into the much larger Twitterverse. Once on Twitter, it went national and even global (at least within the English-speaking countries), producing the mess we all live with today.
I don’t want to tell that entire story here; please listen to the Witch Trials podcast for yourself. It is among the most enlightening things I’ve read or heard in all my years studying the American culture war (along with Jon Ronson’s podcast Things Fell Apart). I just want to note that this story fits perfectly with both the timing and the psychology of Greg’s reverse CBT hypothesis.
Implications and Policy Changes
In conclusion, I believe that Greg Lukianoff was exactly right in the diagnosis he shared with me in 2014. Many young people had suddenly—around 2013—embraced three great untruths:
They came to believe that they were fragile and would be harmed by books, speakers, and words, which they learned were forms of violence (Great Untruth #1).
They came to believe that their emotions—especially their anxieties—were reliable guides to reality (Great Untruth #2).
They came to see society as comprised of victims and oppressors—good people and bad people (Great Untruth #3).
Liberals embraced these beliefs more than conservatives. Young liberal women adopted them more than any other group due to their heavier use of social media and their participation in online communities that developed new disempowering ideas. These cognitive distortions then caused them to become more anxious and depressed than other groups. Just as Greg had feared, many universities and progressive institutions embraced these three untruths and implemented programs that performed reverse CBT on young people, in violation of their duty to care for them and educate them.
I welcome challenges to this conclusion from scholars, journalists, and subscribers, and I will address such challenges in future posts. I must also repeat that I don’t blame everything on smartphones and social media; the other strand of my story is the loss of play-based childhood, with its free play and self-governed risk-taking. But if this conclusion stands (along with my conclusions in previous posts), then I think there are two big policy changes that should be implemented as soon as possible:
1) Universities and other schools should stop performing reverse CBT on their students
As Greg and I showed in The Coddling of the American Mind, most of the programs put in place after the campus protests of 2015 are based on one or more of the three Great Untruths, and these programs have been imported into many K-12 schools. From mandatory diversity training to bias response teams and trigger warnings, there is little evidence that these programs do what they say they do, and there are some findings that they backfire. In any case, there are reasons, as I have shown, to worry that they teach children and adolescents to embrace harmful, depressogenic cognitive distortions.
One initiative that has become popular in the last few years is particularly suspect: efforts to tell college students to avoid common English words and phrases that are said to be “harmful.” Brandeis University took the lead in 2021 with its “oppressive language list.” Brandeis urged its students to stop saying that they would “take a stab at” something because it was unnecessarily violent. For the same reason, they urged that nobody ask for a “trigger warning” because, well, guns. Students should ask for “content warnings” instead, to keep themselves safe from violent words like “stab.” Many universities have followed suit, including Colorado State University, The University of British Columbia, The University of Washington, and Stanford, which eventually withdrew its “harmful language list” because of the adverse publicity. Stanford had urged students to avoid words like “American,” “Immigrant,” and “submit,” as in “submit your homework.” Why? because the word “submit” can “imply allowing others to have power over you.” The irony here is that it may be these very programs that are causing liberal students to feel disempowered, as if they are floating in a sea of harmful words and people when, in reality, they are living in some of the most welcoming and safe environments ever created.
2) The US Congress should raise the age of “internet adulthood” from 13 to 16 or 18
What do you think should be the minimum age at which children can sign a legally binding contract to give away their data and their rights, and expose themselves to harmful content, without the consent or knowledge of their parents? I asked that question as a Twitter poll, and you can see the results here:
Image: See my original tweet.
Of course, this poll of my own Twitter followers is far from a valid survey, and I phrased my question in a leading way, but my phrasing was an accurate statement of today’s status quo. I think that most people now understand that the age of 13, which was set back in 1998 when we didn’t know what the internet would become, is just too low, and it is not even enforced. When my kids started 6th grade in NYC public schools, they each told me that “everyone” was on Instagram.
We are now 11 years into the largest epidemic of adolescent mental illness ever recorded. I know so many families that have been thrown into fear and turmoil by a child’s suicide attempt. You probably do too, given that the recent CDC report tells us that one in ten adolescents now say they have made an attempt to kill themselves. It is hitting all political and demographic groups. The evidence is abundant that social media is a major cause of the epidemic, and perhaps the major cause. It's time we started treating social media and other apps designed for “engagement” (i.e., addiction) like alcohol, tobacco, and gambling, or, because they can harm society as well as their users, perhaps like automobiles and firearms. Adults should have wide latitude to make their own choices, but legislators and governors who care about mental health, women’s health, or children’s health need to step up.
It’s not enough to find more money for mental health services, although that is sorely needed. In addition, we must shut down the conveyer belt so that today’s toddlers will not suffer the same fate in twelve years. Congress should set a reasonable minimum age for minors to sign contracts and open accounts without explicit parental consent, and the age needs to be after teens have progressed most of the way through puberty. (The harm caused by social media seems to be greatest during puberty.) If Congress won’t do it then state legislatures should act. There are many ways to rapidly verify people’s ages online, and I’ll discuss age verification processes in a future post.
In conclusion: All of Gen Z got more anxious and depressed after 2012. But Lukianoff’s reverse CBT hypothesis is the best explanation I have found for Why the mental health of liberal girls sank first and fastest.
The four items are: Life often seems meaningless. The future often seems hopeless. I enjoy life as much as anyone. (reverse coded). It feels good to be alive. (reverse coded). Response options: 1 (Disagree) to 5 (Agree)
See figure 6.69 of Generations, which is due to be published April 25. This is based on Monitoring the Future data.
See figure 6.70 of Generations.
Thanks to David Stein for flagging that the percent rates for “Whenever I Get Ahead, Something or Someone Stops Me” were inconsistent between figures 3 and 4. In Jean’s graph (Figure 3), she included the percentage of respondents who don’t disagree with the statement (i.e., those who answered “neutral,” “mostly agree” or “agree,”) while Zach (Figure 4) only included respondents who answered, “agree.”
The Monitoring the Future study is administered each year, but in all of Zach’s graphs, he merged pairs of years, to increase the sample size and stability of trends as we divided up participants by gender and politics.
The four items are all from the Rosenberg Self-Esteem scale. Gimbrone et al. took four of the 6 negative (self-critical) items, in their search for items to measure internalizing symptoms. They report that this four-item self-derogation scale has a reliability of alpha = .87.








Great, comprehensive, survey about an essential subject!
I saw this syndrome unfolding when my now-32 year old son was taught in his undergraduate cognitive neuroscience class that because the same part of the brain lights up when a person is physically hit or verbally insulted, “science proves that speech is violence”.
We’re dealing with a cultural mood that has found numerous ways to insidiously infiltrate our civilizational consensus. I hope articles like this--evidence-based and data-driven--can help turn the tide, but if not there are bad times ahead.
Random, but for an amazing set of data to support this - check out the Opinion archive for The Tab, an all-UK student newspaper. You can directly see student opinions - and not those of just any students, but of wannabe journalists - change over the past 11-12 years. In 2011 the slant was still very much towards free speech, in 2020 there's an article admonishing Rihanna for appropriating the Qur'an. Everything politics-related is quite moralistic and scold-y in tone now, and echoes the mainstream Guardian/Twitter viewpoint. The writing also gets better and more interesting when you scroll back to 2010!