Kids Who Get Smartphones Earlier Become Adults With Worse Mental Health
New global study from Sapien Labs finds consistent links, stronger for girls
When parents are asked to identify their top fears about the safety of their children, what do you think tops the list? According to a survey last year by Safehome.org, it’s not cars, strangers, or any other physical threat; it’s “internet/social media.” That’s not just for parents of teenagers and pre-teens, whose lives seem to revolve around their phones. It’s even true for parents of younger kids, ages 7-9 because every parent sees it coming and few know what to do about it. Parents don’t want their children to disappear into phones, as so many of their friends' children have; some resolve to wait until 8th grade, or later. Then their child hits them with the main argument that makes parents buckle: “But everyone else has a phone, so I’m being left out.”
For parents who resisted, or who plan to resist, a new report may encourage many more parents to join you: Sapien Labs, which runs an ongoing global survey of mental health with nearly a million participants so far, released a “Rapid Report” today on a question they added in January asking young adults (those between ages 18 and 24): “At what age did you get your own smartphone or tablet (e.g. iPad) with Internet access that you could carry with you?” When they plot the age of first smartphone on the X axis against their extensive set of questions about mental health on the Y axis, they find a consistent pattern: the younger the age of getting the first smartphone, the worse the mental health that the young adult reports today. This is true in all the regions studied (the survey is offered in English, Spanish, French, German, Portuguese, Arabic, Hindi, and Swahili), and the relationships are consistently stronger for women.
We believe these findings have important implications for parents, heads of K-12 schools, and legislators currently considering bills to raise minimum ages or require age verification for some kinds of sites (especially social media and pornography). We’ll address those implications at the end of this post. But first: what did Sapien Labs do, and what did they find?
1. The Sapien Labs Study
Sapien Labs is a non-profit research foundation with the goal of understanding how the rapidly changing social and technological environment is changing human brains and minds. Their main research project has been the Global Mind Project, an ongoing program that tracks mental well-being around the world using a comprehensive assessment of mental health along with questions about demographics and various cultural, technological, and lifestyle factors. They have issued a variety of reports on the state of mental health around the world. Among their most important findings is that in all the regions they’ve studied, mental health is worst for the youngest generations.
It didn’t used to be this way. There is a well-known finding in happiness research that, across nearly all nations, happiness or well-being forms a U-shaped curve across the lifespan (See Rauch, 2018). Young adults and people in their 60s and 70s are happier than those in middle age. But that may be changing, especially for women, as Gen Z (born in and after 1996) enters young adulthood. You can see the sudden collapse of young adult mental health in some of our previous posts on this Substack. For example, Figure 1 shows that up until 2011, young Canadian women were the most likely to report having excellent or very good mental health. By 2015 they were the least likely, and the decline in their self-reported mental health accelerated after that, while it changed very little for older women. (The same pattern holds for Canadian men, but to a lesser degree.)
Figure 1. Percent of Canadian women reporting excellent or very good mental health, by age group. Canadian Community Health Survey (2003-2019). Graphed by Zach Rausch.
Why would this be? What changed in the early 2010s that could have rapidly reduced the mental health of teens around the world, with a bigger impact on girls? At the After Babel Substack, we have argued that the sudden switch of teen social life from flip phones (which are designed for communication) to smartphones (which enabled continuous access to social media and much higher levels of phone addiction), is the major cause, though not the only one. There are unique factors at work in each country, but we know of no alternative that can explain the synchronized, gendered, and global decline in teen mental health.
At Sapien Labs, they decided to test the smartphone hypothesis by adding a question about the age at which people got their first smartphone (or tablet). Is it just a coincidence that the first global generation to grow up on smartphones became the first global generation to have lower well-being than the one before them?
Sapien Labs uses a comprehensive assessment of mental well-being that asks participants about 47 elements of mental, social, and emotional functioning on a life impact scale. These 47 elements are aggregated into a single score called the Mental Health Quotient (MHQ), which gives extra weight to patterns that indicate severe problems. It also uses subsets of these 47 elements to create scores along six domains: Mood & Outlook, Social Self, Adaptability & Resilience, Drive & Motivation, Cognition, and Mind-Body Connection.
(You can take the MHQ yourself and you can request access to the full dataset. For scoring and validation of the MHQ, see Newson, Pastukh, & Thiagarajan, 2022, and see this blog post that offers a clear explanation of how the MHQ is scored, and why.)
Figure 2 shows the most basic result in the report: they simply plotted the responses from the nearly 28,000 participants who answered the “first phone” question, from all countries combined.
Figure 2. As age of first smartphone goes up, so does the mental health reported by young adults, assessed by the MHQ. Data from SapienLabs.org.
MHQ scores are calculated from responses to the 47 questions and converted to a scale that runs from -100 to 200, as shown here:
As you can see, the respondents who got their first smartphone before they were 10 years old are doing worse, on average, than those who didn’t get one until they were in their teens. The most mentally healthy respondents are those who did not get a phone until their late teens.1 You can also see that the slope is steeper for young women than for young men. The Gen Z women who got their first smartphone before they were 9 years old are in negative territory, on average.
The power and unique contribution of the Sapien Labs dataset come from two features of their work: First, they use a far more detailed measure of mental health than is used in most other large surveys. The second important feature is their international coverage. So, let’s zoom in and explore the six domain scores that make up the MHQ, first for the global sample, and then for the region and culture we know best: the Anglosphere.
2. Domains of Functioning
As you’ll see if you read the full report, the next step after examining the overall MHQ scores is to examine scores on the six domains of mental functioning:
Mood & Outlook: Includes items about optimism, calmness, anxiety, mood swings, sadness, and anger.
Social Self: Includes items about self-worth, relationships with others, empathy, cooperation, aggression toward others
Adaptability & Resilience: includes items about adaptability to change, ability to learn, and emotional resilience.
Drive & Motivation: Includes items about motivation, curiosity, enthusiasm, and addictions.
Cognition: Includes items about memory, decision-making and risk-taking, focus, and concentration, unwanted thoughts, hallucinations
Mind-Body Connection: Includes items about sleep quality, energy level, appetite, and physical health issues.
Figure 3 shows that for young women, all six domain scores show the same basic pattern as the MHQ: a consistent rise. You can also see that a few of the domains seem to rise more slowly or level off somewhat after the age of 13 or 14: Drive and motivation, Mind-body connection, and Cognition. However, the other three dimensions continue to rise all the way to age 18. The domain that rises fastest, meaning that it is most highly correlated with age of first smartphone, is the “social self” domain.
Figure 3: The 6 domains of well-being, for young women, as a function of when they got their first smartphone. From SapienLabs.org.
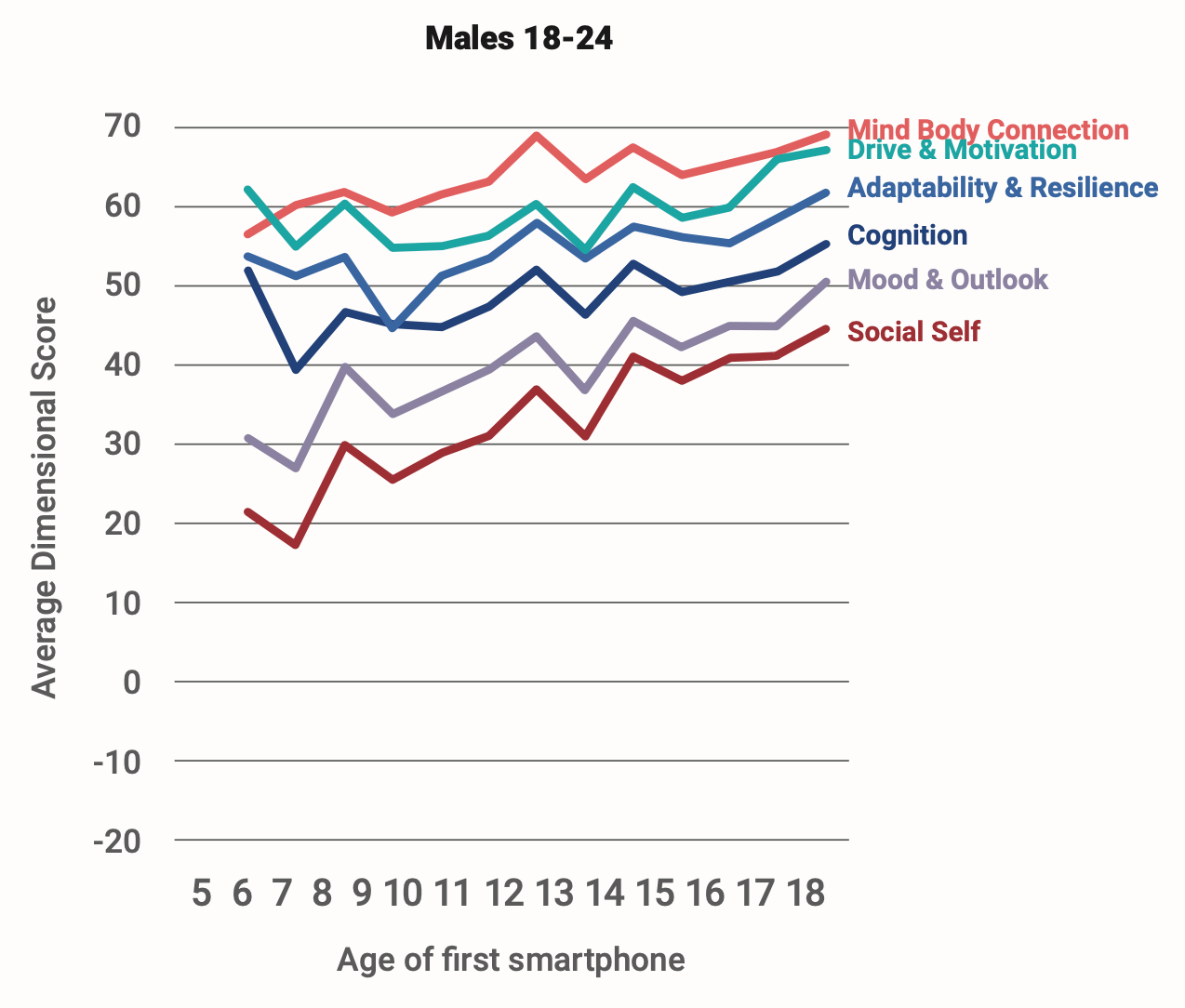
Figure 4 shows the same analysis for young men. The pattern is similar, with two important exceptions. First, the slopes are substantially lower, meaning that the mental health and well-being of young men are not as strongly related to the age at which they got their first smartphone as it is for their sisters, although it is still related. (All of the significance tests and effect sizes can be found in supplementary materials posted in this Google Drive link.2) The second difference is that all of the lines are higher for boys, meaning that boys are doing better than girls at all ages (at least, according to their self-reports). The one exception is that the line for Adaptability & Resilience reaches the same level for both sexes by age 18. Given the steeper slopes of all six lines for girls, this means that sex differences in adult mental health are larger among those who got a smartphone earlier.
Figure 4: The 6 domains of well-being, for young men, as a function of when they got their first smartphone. From SapienLabs.org.
One major issue in analyzing an international dataset is that there are just so many differences between countries, regions, and religions that there are many opportunities for confounding variables to lead us astray. For example, in the Sapien Labs dataset, in the less wealthy countries such as India, few young adults had received a smartphone before the age of 10, which means that the data points on the left sides of the graphs contain almost no Indians, whereas the data points on the right side (no phone until 17 or 18) contain many Indians and fewer from the USA. If Indians are mentally healthier than Americans (for other reasons), this could cause the lines to slope even if smartphones had no effect on mental health. It is important, therefore, to look at individual countries and regions. (The Sapien Labs report does this in its appendix, where you can see that the trends hold for each of the world regions).
The region that we (Jon and Zach) know best and have written on extensively is the Anglosphere (the English-speaking countries of The United States, Canada, The United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and sometimes Ireland). We, therefore, decided to examine what Sapien Labs had found about those countries and compare it to what we have found.
3. Zooming in on the Anglosphere
At the After Babel Substack, we have been documenting the patterns of rising mental illness among teens around the world, and, like Sapien Labs, we have found that the sudden decline of teenage mental health is an international phenomenon. Our research so far indicates that the increases in mental illness in the 2010s were slightly larger in the Anglosphere than in any other region we’ve examined. Figure 4 shows the large and sudden rise in self-harm rates among teens, particularly girls, in four of these nations (you can see much more in Zach’s initial report on the Anglosphere).
Figure 5. Since 2010, rates of self-harm episodes have increased for teens in the Anglosphere countries. For data on Australia and for all sources, see Rausch and Haidt (2023).
In every Anglosphere country, the mental health of teens declined sharply around the same time (~2012) and in the same way (depression, anxiety, and self-harm, with bigger increases for girls). We have also found that the five Nordic nations show similar trends, particularly when examining changing rates of depression and anxiety (though not always for self harm).
The Sapien Labs study began in 2019 so it cannot show us trends since 2010, but it can show us how young adults are doing today, and it can link variations in mental health today to variations in age of first smartphone. We wanted to get more familiar with the data and examine these links for ourselves, so we downloaded the full dataset as it was available on their Brainbase site on May 13, 2023, which was just about 2 weeks later than the dataset used in the Sapien Lab report. Our dataset contains 1,798 more participants, for a total of 29,767. The number of participants from the six anglosphere countries was much smaller: 1,465 (823 females, 584 males). By country: 682 in the USA, 297 in the UK, 224 in Canada, 239 in Australia, 10 in New Zealand, and 13 in Ireland.
We cleaned and organized our dataset in the same way as the team at Sapien Labs, with a small modification to account for our much smaller sample size. To reduce the jerkiness of the graph lines when we drop down to lower numbers of respondents for each point, we grouped participants into 2-year buckets (or three years, for our youngest bucket, 5-83). Figure 5 shows that the MHQ scores of Anglosphere boys and girls show patterns very similar to those reported in Figure 1 by Sapien Labs for the full 28,000-person international sample: The later the age of smartphone acquisition, the better the mental health. At least, that is true for the girls, all the way up to 18. For Anglosphere boys, there is a leveling off after the 11-12 mark. Delays beyond age 12 do not seem to be related to further increases in MHQ scores.4
Figure 6. Anglosphere countries only: As age of first smartphone goes up, so does the mental health reported by young adults, especially for women. Data from SapienLabs.org, graphed by Zach Rausch.
We also plotted the six MHQ domain scores and found similar results. For females, all six dimensions of mental well-being improve as the age of smartphone acquisition increases.5 The effects are particularly strong for the “social self” and “mood and outlook”, which correspond well to the rise of internalizing disorders (depression and anxiety), which Zach has shown is rising within every Anglosphere nation.
Figure 7. Anglosphere countries only: female MHQ dimension scores. Well-being on all 6 dimensions increases as age of smartphone acquisition increases.
The trends for boys are similar to girls, though the effects are smaller and there is more fluctuation.6 Figure 8 shows that at the youngest ages, increasing age corresponds with improvements in each of the six dimensions. However, for boys, improvements tend to level off after age 12.
Figure 8. Anglosphere countries only: male MHQ dimension scores. Changes are smaller and more varied compared to females.
4. Limitations
It’s important to note that the report from Sapien Labs is one of their “rapid reports” made possible by their fast-growing number of participants and the easy access they offer to their data. They added the question about age of first smartphone in January and they are publishing a report, with data from nearly 28,000 participants, in May. We believe that this ability to move quickly is a public service during a global pandemic of teen mental illness. While their rapid report is not a standard academic publication and has not been through peer review (which often takes a year or more), the open access to the data has allowed us to investigate and confirm the trends they are reporting. We hope and expect that other researchers will download the dataset and offer critiques of the data, the analyses, and the conclusions drawn. This sort of “post-publication peer review” is becoming increasingly common as the problems with the existing peer review system become more widely known.
One issue to keep in mind with the Sapien Labs dataset is that the participants in each country are not a random or representative sample of the people in that country. Such studies would be extremely expensive to run, and now that so few people agree to phone solicitations or even answer their phones, it is unclear how representative such surveys can be. Those who agree to be interviewed, or who are motivated by money to participate, are not representative of the broader population. For this Sapien Labs report, participants came to the site on their own, or from online advertisements paid for by Sapien Labs, for the purpose of getting a detailed report on their wellbeing. So, the means reported for any country should not be treated like direct measures of the true means. However, samples such as these are still very useful for examining differences within the sample, such as those between men and women, or between those who got a smartphone early and those who got one late. And the much larger size of the Sapien Labs dataset, compared to Gallup and other survey organizations, allows for many additional analyses.
A second factor to keep in mind is that like all surveys, what we get is correlational data that is open to alternative interpretations. The graphs in the report are likely to suggest to most readers that getting a smartphone early causes later mental health problems. But with correlational data we must always consider the possibility that the causal arrow could run in reverse. In this case: having low well-being as a young adult could cause people to believe that they got a smartphone earlier than they did, but this seems unlikely. We must also always consider that there could be “third variables” that cause both of the first two variables to rise. In this case, one plausible confounding third variable is permissive parenting. Perhaps permissive parents (in each country) simultaneously do two things: they give their kids smartphones at very young ages, and they also give them few boundaries and little structure, which then interferes with development and produces struggling young adults. While this hypothesis is plausible and should be investigated, it is not clear how it would explain the fact that, in all the regions studied, it is the girls who show a tighter connection between early phone acquisition and later mental health problems, just as it is the girls who show a tighter connection between heavy social media use and concurrent mental health problems. Nor would it explain why mental health dropped so rapidly in the early 2010s (especially for girls) if permissive parenting (or some other variable about family life) was the real culprit.
And finally, we note that no one study is definitive, and more research is needed. We have been able to find a few other studies that examined the age at which children got their first smartphones (We have created a new appendix [8.14] in our collaborative review doc on Social Media and Mental Health). So far they are mostly smaller studies that have produced mixed results. If you know of any others, please add them to the doc or put a link to them in the comments below. We want to get this right.
5. Implications
We cannot be certain that the correlations shown in the data are evidence of causality, but we think it is appropriate for those who care for children to act on the preponderance of the evidence (which is the standard in a civil trial) rather than waiting for evidence beyond a reasonable doubt (which is the standard used in a criminal trial. See proposition 2 in this post.) There is increasing evidence that smartphones have a variety of detrimental effects on child development including reductions of sleep, focus, and time with friends in person, along with increases in addictive behaviors, so it makes sense that the cumulative effect of getting one’s first phone in elementary school would be larger than for those who don’t get a phone until high school. This is an important point made in the Sapien Labs report: The relationships they find suggest that there is a cumulative effect of having had a smartphone (and its many apps) over many years of childhood; they do not represent the effects of having used a phone a lot in recent days or weeks (which is the focus of most of the published research).
We think the implications for action are strongest for policies related to children and younger teens––those still in elementary and middle school (that is, age 14 and below) In most of the graphs in this post, including those for the Anglosphere, the slopes of the lines are steepest for those ages, and the links are visible for boys as well as girls (though smaller for boys). This concern to protect children before and during early puberty is consistent with a study published last year which found that in a large longitudinal study of British adolescents, the peak years for evidence of links between social media use and lower satisfaction with life were 11-13 for girls (which corresponds to the early part of puberty), while for boys (who begin puberty a bit later) it was 14-15.
On the other hand, the implications for action related to older teens and especially boys are less clear, at least within the United States and other Anglosphere nations. The lines for boys are somewhat flat in those ages, and the increases for girls generally slow down too. Furthermore, the arguments for why high school students need a smartphone (rather than an alternative, such as a flip-phone) are stronger than the arguments for why elementary and middle school students need one.
We, therefore, believe that the Sapien Labs findings should motivate us to think carefully about whether and when to give children their own smart devices, especially before high school. It is not the Internet per se that is harmful; so much of the internet is fantastically educational, useful, and entertaining. The most relevant questions, we think, are: 1) At what age do you want to give a child continuous access to the internet and social media, even when away from home, even when sitting in class? 2) At what age do you want to give social media companies, and other companies, continuous access to a child’s attention? And 3) does a child really need a smartphone when other kinds of phones (such as “flip phones” or Light Phones) work just as well for general communication (phone calls and texting)?
Implications for Parents
The group Wait Until 8th was founded to solve the collective action problem that parents and teens are in: Even if most parents wanted to wait until high school to give their children smartphones and social media, as long as most kids have those things by 6th grade, there will be enormous pressure on their children, and hence on the parents, to relent. Unless the parents can coordinate. So Wait Until 8th asks parents to sign a pledge, when their children are in elementary school, that they will wait until 8th grade to give them a smartphone. The pledge only takes effect once ten families in that child’s grade have signed the pledge so that the child will have a community of peers and will not feel so isolated before 8th grade.
We think this is a great idea, we just suggest that the pledge should be: Wait Until 9th. Or Wait Until High School. Children are usually 12 or 13 at the start of 8th grade; that is still within the period of early puberty. Plus, if 8th graders have smartphones, that means that smartphones will be everywhere in middle schools, increasing the desire of 7th graders to get them. To solve collective action problems, we think it’s best to focus on setting good norms within collectives (such as schools): make elementary schools and middle schools be smartphone free.
Parents understandably want to be able to reach their children when they are away from home, and a flip phone or other “dumbphone” is a very reasonable first phone that allows parents and children to reach each other. We suggest that parents not give smartphones as first phones. Let children learn to master a simpler kind of phone, one that cannot be loaded with addictive apps. Wait Until 8th offers an excellent list of the many smartphone alternatives.
Implications for Schools
Many of the teachers and heads of schools that Jon talks to are bitter about the effects of smartphones on their students and their school culture. They complain about the constant drama unfolding on social media during the school day. They complain about the distraction and the increased difficulty of getting students’ attention during class, since many students sneak looks at their frequently-buzzing phones, especially those sitting in the back rows. Many schools say that they ban phones, but what they often seem to mean is “the rule is that you can’t take out your phone during class.” That means that some students (the ones most suffering from phone addiction) will learn to do it stealthily, and many of the rest will just pull out their phones as soon as class is over, thereby missing out on face-to-face interactions with the students right next to them.
We suggest that schools consider going phone free, meaning that students can use their phones to arrive and depart from school, but once they enter, their phones (smart or dumb) would be placed in a phone locker, or in a lockable pouch. We think the case for doing this in elementary schools and middle schools is strongest. In a few weeks, Jon will write a substack post laying out the empirical evidence that smartphones distract students and disrupt education, even when they are kept in students’ pockets.
We also suggest that school districts collaborate with social scientists to do experiments on entire schools, rather than on individual students. What if a state or district identified 20 middle schools that were willing to cooperate, and then randomly assigned half of them to go phone free? There is no research of this kind that we can find, yet such a simple study would give us results within a single year that could potentially yield findings that improve both mental health and educational outcomes.
Implications for Legislatures
If there is a cumulative effect of smartphone ownership in childhood, and if the effect is due in part to heavy use of certain kinds of apps (such as social media) rather than other kinds of apps (such as watching movies, or using Wikipedia), then it becomes even more vital that we develop ways of age-gating certain apps and content. At present, US law sets a minimum age of 13 at which children can sign contracts with companies to give away their data (when they check a box on the terms of service). But the law was written such that the companies are not required to verify ages. As long as a child says that she is 13 or older, she’s in and can create a social media account.
This must change. If the minimum age were enforced, it would help parents solve their collective action problem, at least with regard to Instagram, Tiktok, and other social media sites for underage users. It is precisely Congress’s failure to enforce the age 13 rule that puts parents in the trap. Many states are now introducing legislation to remedy this omission. And there is one federal bill that does a particularly good job of focusing on age limits and age verification: The Protecting Kids on Social Media Act, introduced by Senators Schatz (D-HI), Cotton (R-AR), Murphy (D-CT), and Britt (R-AL). The act would “set a minimum age of 13 to use social media apps and would require parental consent for 13 through 17 year-olds. The bill would also prevent social media companies from feeding content using algorithms to users under the age of 18.” The bill also requires social media companies to develop rigorous age verification methods. (There are already many in existence, and many more would appear if the bill gets passed.) We also think the Kids Online Safety Act of 2022, introduced by senators Blumenthal (D-CT) and Blackburn (R-TN) would do a lot to make social media less damaging to children, and easier for parents to control. The fact that so many bills are bipartisan, at both the state and federal level, is a very encouraging sign in our polarized time. Legislators often report seeing the problems in their own children.
In conclusion: there is a great deal that can be done, individually and collectively, to address one of the top fears that parents express, about the safety and health of their children. The Sapien Labs data offers us new insight into the nature of the problem, and it alerts us that the problem may be global. It also guides us to the ages at which reform efforts are most likely to work.
POSTSCRIPTS (added on May 18, 2023)
1—We welcome additional and deeper analyses of the Sapien Labs data, and will post links here to such reports whether they support or contradict our analyses in this post.
2—One issue we should have discussed in the text is the inclusion of tablets, along with smartphones, in the Sapien Labs’ questionnaire. If their findings differ from those of other labs which asked only about age of first smartphone, then we won’t know whether part of the difference is the inclusion of tablets. We hope that future studies will ask about the two devices separately to figure out which devices are associated with harm at which ages (if any).
3—Some commentary online has made the important point that it’s not the phone itself which is harmful; it is the particular apps that the child uses, a child with a particular personality, in the context of a particular family that does (or does not) exercise oversight and apply restrictions. We agree. The original iPhone introduced by Steve Jobs was three devices: a phone, an iPod, and a web browser. Great! Three tools. Probably not harmful. It’s the addition of the app store that turned the smartphone into a portal to everything. If early acquisition of a smartphone is shown to be reliably associated with developmental problems, it would likely be because it enables continuous 18-hour-per-day access to hundreds of activities.
There are relatively few participants who did not get a phone until after the age of 18, especially in developed nations. These participants were cut from the analysis, in the report, and in our analyses below.
This includes statistical tests between each age for each score and problem rating, as well as correlations and population trend statistics for both linear and logarithmic fits.
We dropped all participants who gave an age of first smartphone that was above 18 or below age 5. There were relatively few on both ends.
Using simple Pearson correlations, all 6 domain scores correlate significantly with age of phone acquisition at p < .01, except for mind-body connection, which correlates p < .05.
Using simple Pearson correlations, only two of the six domains correlate significantly with age of phone acquisition (both p < .05): cognition, and mind-body. We then tested the hypothesis that for boys, the correlation is confined to the earlier years (ages 5-14), as discussed below. When we examined just those participants, in the Anglosphere, we found that age of first smartphone was significantly correlated with the MHQ, and with the domains of adaptive resilience, and mood-outlook, all at p < .05. See our corresponding Google Doc for relevant correlation matrices.
Using simple Pearson correlations, only two of the six domains correlate significantly with age of phone acquisition (both p < .05): cognition, and mind-body.











I work in behavioral health and most of my career my work has been with teens and young adults. I have never been more concerned than I am right now. I specialize in working with people with substance use disorders, particularly those with trauma backgrounds. The anhedonia that I see in young people is frightening. Many of my clients literally have no engagement with the “outside world” other than through digital media. Their friends are “online,” they don’t work, they don’t know what they want to do, they can’t articulate any goals. They don’t want to get driver’s license because it’s too scared and causes anxiety. They don’t have the skills to move out and live on their own. They don’t socialize with anyone outside of the home. They’re afraid to try new things. They are content to look at their phones and play video games. I’ve made it part of my intake now, when working with depressed teens and young adults, I immediately start probing into time spent online. It seems like they’re either checking out digitally or checking out with drugs and alcohol. But either way, they view the world and the expectations of adult life to be scarey and overwhelming.
"Parents understandably want to be able to reach their children when they are away from home"
Is this in fact understandable? I would assume that the parents of just about everyone reading this piece had neither the ability, nor likely the desire to be able to directly reach their children when they were away from home. We survived.
The desire to get in touch with your kids directly when they're outside the home strikes me as a symptom of helicopter parenting and a potential pretext for caving on the smartphone front.